Developer Guide
ForgetfulNUS is a desktop glossary app for students taking German 1 (LAG1201) and German 2 (LAG2201) in NUS to practise and test their vocabulary, optimised for use via a Command Line Interface (CLI). * This project is based on the AddressBook-Level3 project created by the SE-EDU initiative.
Table of Contents
- Setting Up, Getting Started
- Design
- Implementation
- Documentation, Logging, Testing, Configuration, Dev-Ops
- Appendix: Requirements
- Appendix: Instructions for Manual Testing
Setting Up, Getting Started
Refer to the guide Setting Up and Getting Started.
Design
Architecture
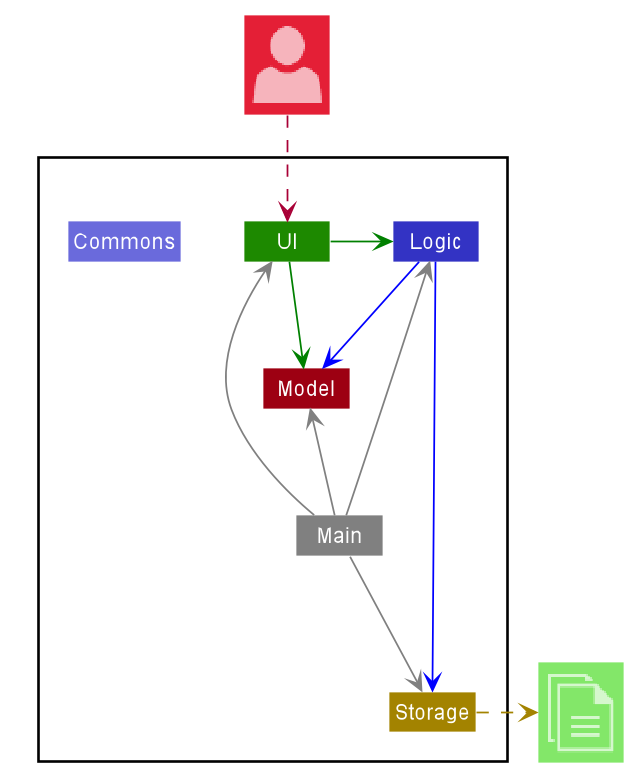
The Architecture Diagram given above explains the high-level design of the App. Given below is a quick overview of each component.
.puml files used to create diagrams in this document can be found in the diagrams folder. Refer to the PlantUML Tutorial at se-edu/guides to learn how to create and edit diagrams.
Main has two classes called Main and MainApp. It is responsible for,
- At app launch: Initialises the components in the correct sequence, and connects them up with each other.
- At shut down: Shuts down the components and invokes cleanup methods where necessary.
Commons represents a collection of classes used by multiple other components.
The rest of the App consists of four components.
-
UI: The UI of the App. -
Logic: The command executor. -
Model: Holds the data of the App in memory. -
Storage: Reads data from, and writes data to, the hard disk.
Each of the four components,
- defines its API in an
interfacewith the same name as the Component. - exposes its functionality using a concrete
{Component Name}Managerclass (which implements the corresponding APIinterfacementioned in the previous point. For example, theLogiccomponent (see the class diagram given below) defines its API in theLogic.javainterface and exposes its functionality using theLogicManager.javaclass which implements theLogicinterface.
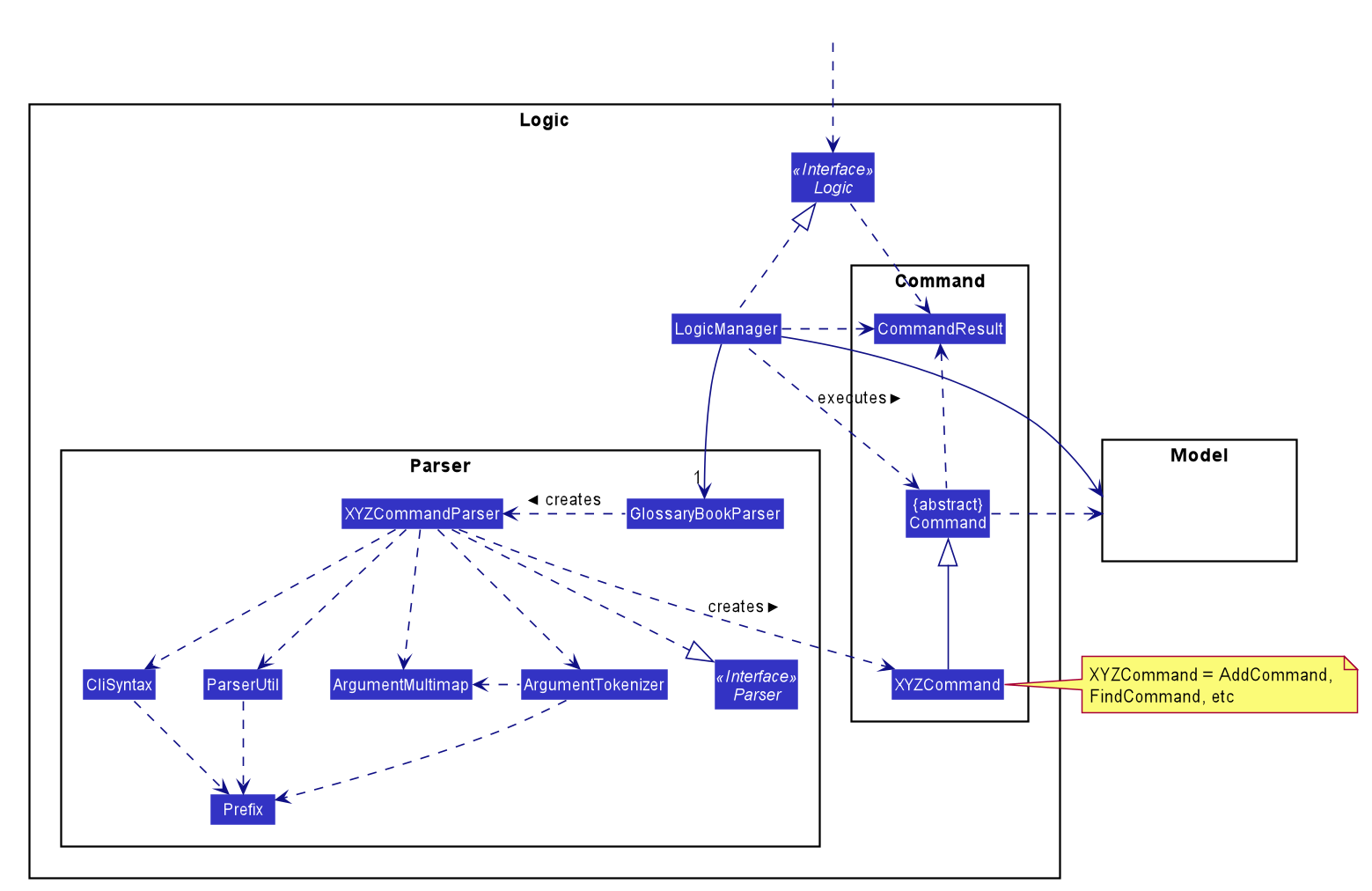
How the architecture components interact with each other
The Sequence Diagram below shows how the components interact with each other for the scenario where the user issues the command delete 1.
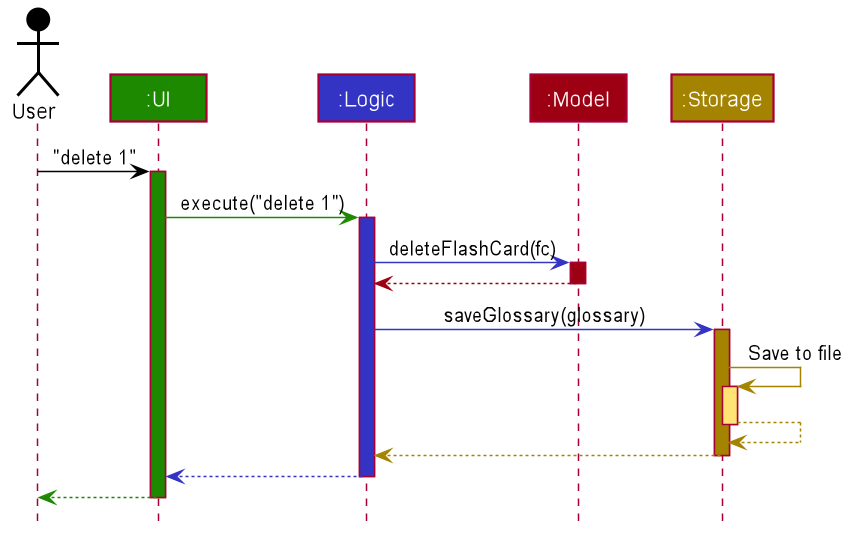
The sections below give more details of each component.
UI Component
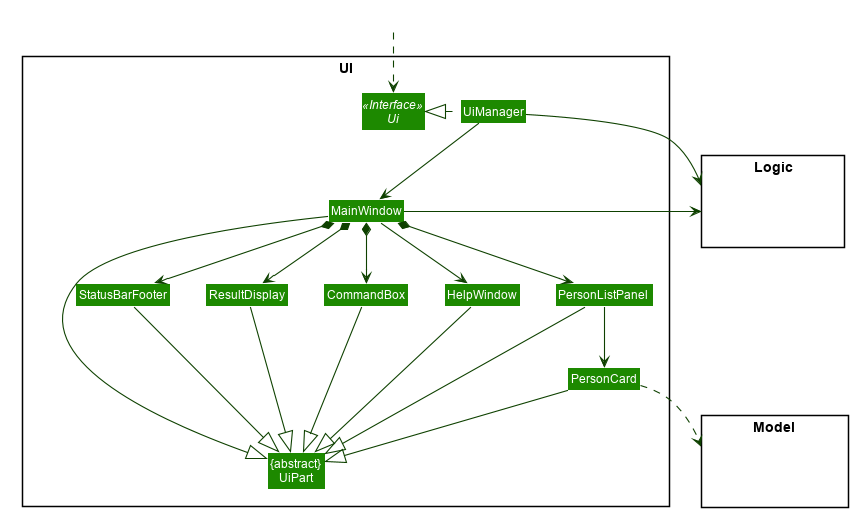
API :
Ui.java
The UI consists of a MainWindow that is made up of parts e.g.CommandBox, ResultDisplay, PersonListPanel, StatusBarFooter etc. All these, including the MainWindow, inherit from the abstract UiPart class.
The UI component uses JavaFx UI framework. The layout of these UI parts are defined in matching .fxml files that are in the src/main/resources/view folder. For example, the layout of the MainWindow is specified in MainWindow.fxml
The UI component,
- Executes user commands using the
Logiccomponent. - Listens for changes to
Modeldata so that the UI can be updated with the modified data.
Logic Component

API :
Logic.java
-
Logicuses theGlossaryBookParserclass to parse the user command. - This results in a
Commandobject which is executed by theLogicManager. - The command execution can affect the
Model(e.g. adding a Flashcard). - The result of the command execution is encapsulated as a
CommandResultobject which is passed back to theUi. - In addition, the
CommandResultobject can also instruct theUito perform certain actions, such as displaying help to the user.
Given below is the Sequence Diagram for interactions within the Logic component for the execute("add g/German e/English") API call.
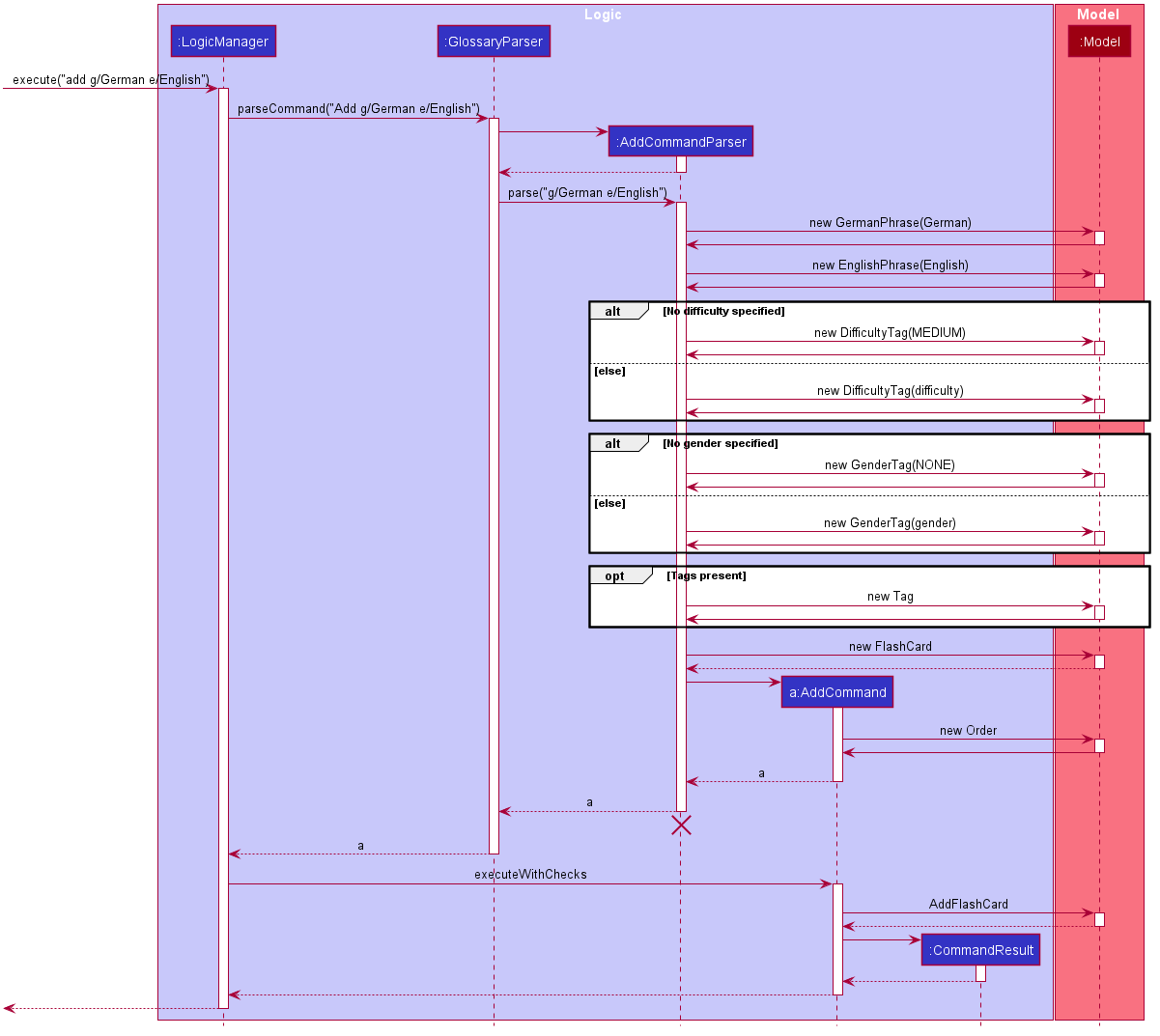
AddCommandParser should end at the destroy marker (X) but due to a limitation of PlantUML, the lifeline reaches the end of diagram.
Model Component
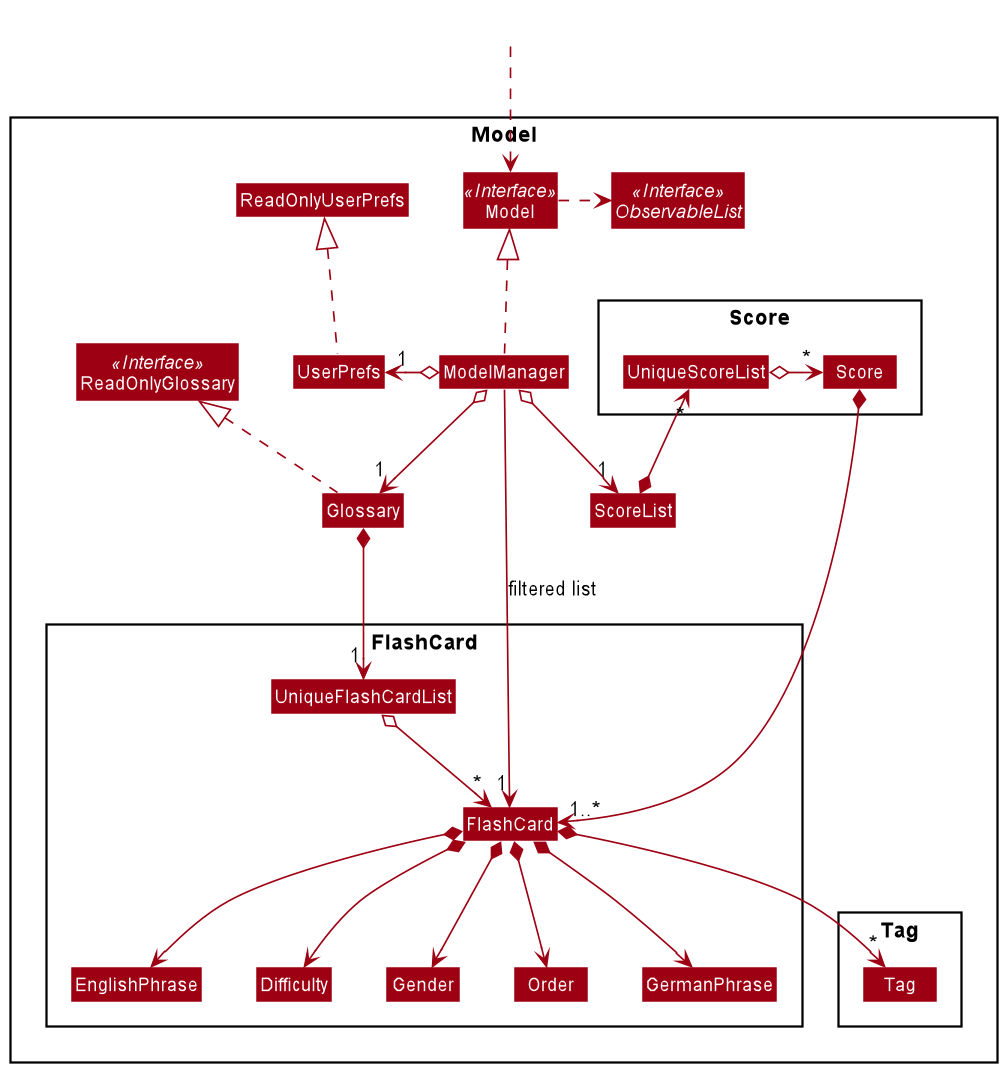
API : Model.java
The Model,
- stores a
UserPrefobject that represents the user’s preferences. - stores the glossary data.
- exposes an unmodifiable
ObservableList<Flashcard>that can be ‘observed’ e.g. the UI can be bound to this list so that the UI automatically updates when the data in the list change. - does not depend on any of the other three components.
Storage Component
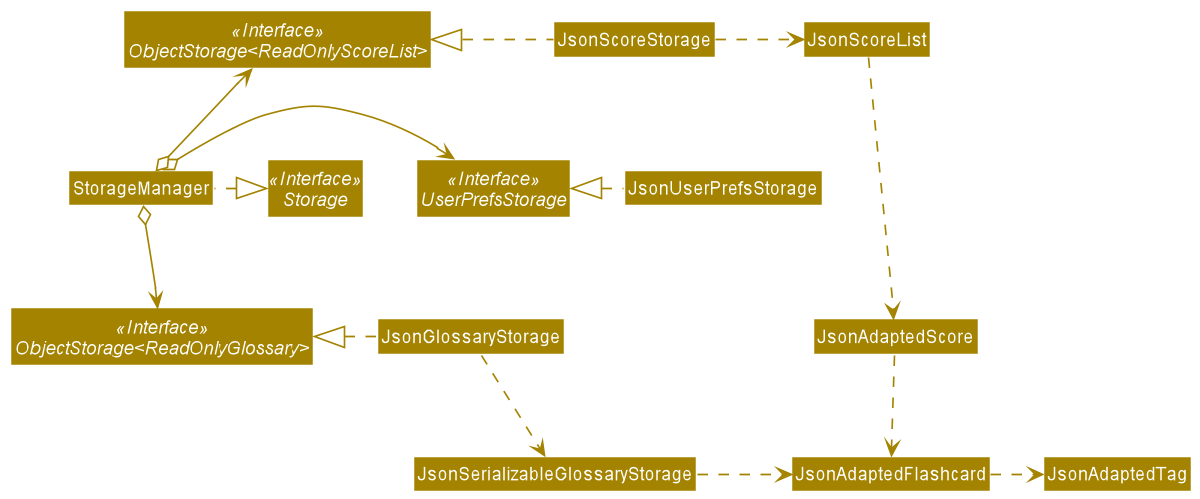
API : Storage.java
The Storage component,
- can save
UserPrefobjects in json format and read it back. - can save the address book data in json format and read it back.
- can save the user scores data in json format and read it back.
JsonAdaptedFlashCard and JsonAdaptedScore are Json-friendly versions of
the Model’s respective FlashCard and Score classes. Similarly, JsonScoreList and
JsonSerializableGlossary are Json-friendly versions of the Model’s respective UniqueFlashCardList and UniqueScoreList classes. These Json-friendly classes handle Json serialization and deserialization, so glossary and score data can be saved and read from their respective .json files.
Common Classes
Classes used by multiple components are in the seedu.forgetfulnus.commons package.
Implementation
This section describes some noteworthy details on how certain features are implemented.
Predefined Tags
This feature is facilitated by PredefinedTags, DifficultyTag and GenderTag.
There are two types of predefined tags for each flash cards. They are the DifficultyTag and GenderTag.
The following class diagram outlines the structure of the predefined tags and how it interacts with other Model components.
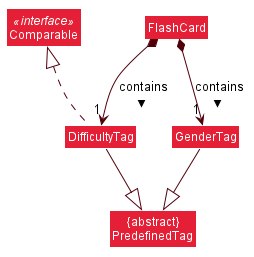
To go for a more OOP solution, both DifficultyTag and GenderTag were made to extend from an abstract class PredefinedTag.
Referring to the class diagram above, note that DifficultyTag also implements Comparable for use in the sorting feature. As ForgetfulNUS does not support sorting by GenderTag, it does not implement Comparable.
The following activity diagram summarises what happens for the DifficultyTag when a user executes the Add command:
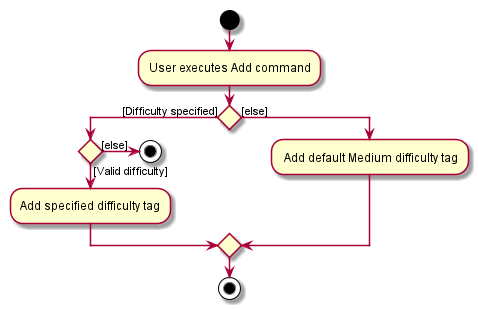
For GenderTag the activity diagram is similar, with the default tag being set to NONE instead. Note that even if a flashcard does not appear to have a GenderTag on the UI, each flashcard will always have a GenderTag. The UI will just not display anything for a NONE state.
Quizzing
The proposed quiz feature for users to test their vocabulary is facilitated by Model and Command. It does so by allowing a command to set Model to quiz mode. When the model is in quiz mode, it will take in commands allowing users to attempt to type the correct definition, skip the flashcard under test or end the quiz.
It implements the following operations:
-
Glossary#quiz(Model)— Starts the quizzing with the displayed flashcard list. -
Glossary#try(Model)— Attempt to type the correct English definition of the German phrase on the current flashcard. -
Glossary#next(Model)— Skips the current flashcard under test. -
Glossary#end(Model)— Ends the quiz.
These operations are exposed in Ui as commands. They are implemented by QuizCommand, TryCommand, NextCommand and EndQuizCommand respectively.
Given below is an example usage scenario and how the quiz mechanism behaves at each step.
Step 1: The user launches the application with an existing list of flashcard. Flashcards from this list will be tested in the order of their index, and the list can be customised by using the find <search phrase> command.
Step 2: User enters quiz and the program will execute the QuizCommand on the current model. The model will be set to quiz mode and will be expecting quiz commands like try <attempt>, next and end. The Ui will update to hide all the English definitions on the flashcards. The first flashcard on the list will be tested when the quiz begins.
Step 3: The user enters try <attempt> and the GlossaryParser#parse(String) will parse input into a TryCommand with the attempt. If the attempt matches the English definition of the flashcard, the flashcard index, score and question count in model increment. The Ui will update to show the English definition of the current flashcard. The next flashcard on the list will be tested.
If the attempt does not match, step 3 will repeat.
Alternatively, the user can enter next to execute the NextCommand on the model. The flashcard index and question count in model will increment, the Ui will update to show the English definition of the current flashcard andthe next flashcard and the next flashcard will be tested.
Step 4: The quiz mode will end when there is no next flashcard i.e. current flashcard is the last on the list, and the user attempts the English definition correctly with try <attempt> or the user skips the card with next. Alternatively, the quiz can be ended early at any point during the quiz when the user enters end, letting the program execute the EndQuizCommand on the current model. The Ui will update to show the English definitions on all the flashcards in the flashcard list.
The following activity diagram outlines the process of quizzing:
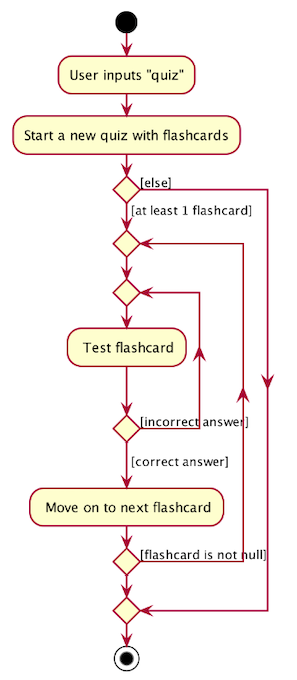
The following sequence diagram shows how the quiz operation works with respect to the logic component:
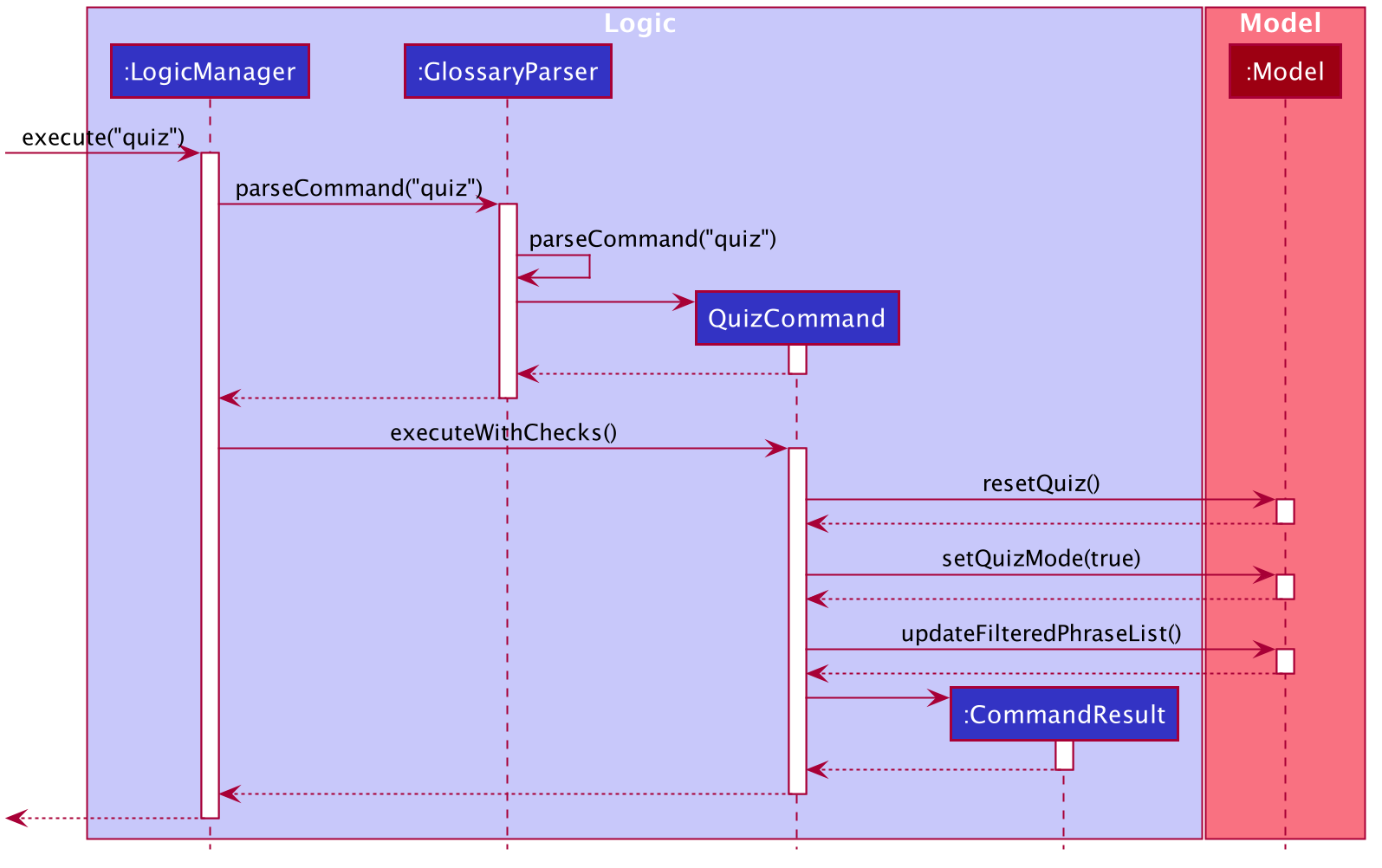
Quizzing also works in tandem with find and sort features, allowing users to limit the phrases tested and change the order of testing.
During quizzing, only try, next and end commands are allowed to be used. All other commands except help and exit will remind the user that they are in quiz mode and to end the quiz first before using any other commands.
Random Quizzing
This feature is facilitated by RandomQuizCommand and RandomQuizCommandParser and Model.
RandomQuizCommand implements the method:
-
RandomQuizCommand#execute(Model)— Returns aCommandResultwhich begins a round of vocabulary quiz containing the specified number of flashcards randomly selected from the existing glossary.
RandomQuizCommandParser implements the method:
-
RandomQuizCommandParser#parse(String)— Returns aRandomQuizCommandwhich ensures the specified number of flashcards is valid.
Model implements the method:
-
Model#setRandomQuizMode(boolean)— Sets the state of Model to randomQuizMode and backs up or retrieves the original glossary depending on the boolean value.
Given below is an example usage scenario and how the random quiz mechanism behaves at each step.
Step 1. The user launches the application with an existing glossary of flashcards that the user added previously.
Step 2. The user executes random 5 command to randomly select 5 flashcards from the existing glossary to test his/her own vocabulary. The random 5 command calls RandomQuizCommandParser#parse(String) which checks the validity of the argument given to random command. This then leads to the calling of RandomQuizCommand#execute(Model), which in turn calls the Model#setRandomQuizMode(boolean).
Step 3. The change of state of the Model resulting from Model#setRandomQuizMode(boolean) starts a round of vocabulary quiz for the user when the boolean parameter provided is true.
The following sequence diagram shows how the random quiz mechanism works:
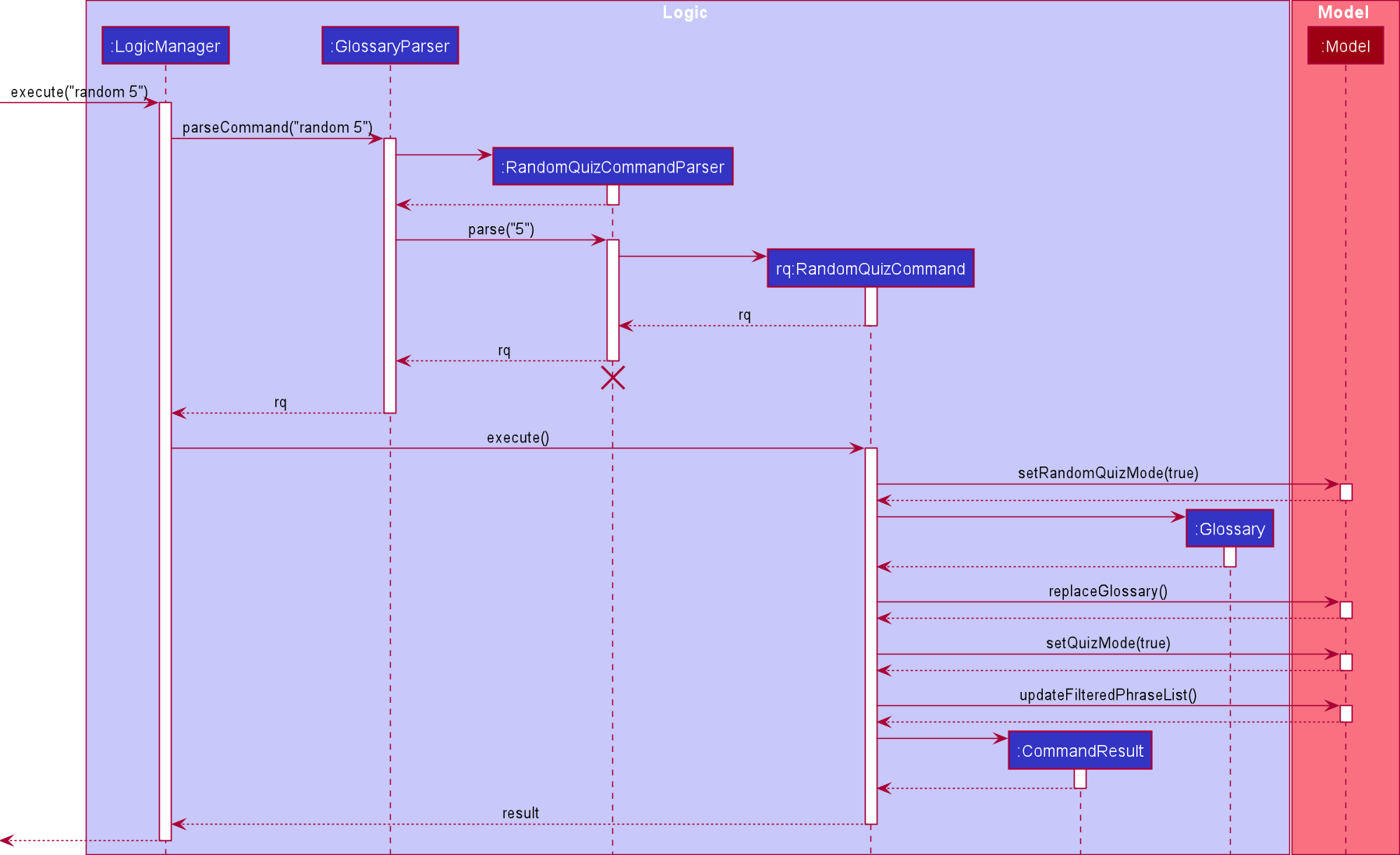
The following activity diagram summarises what happens when a user executes the random command:
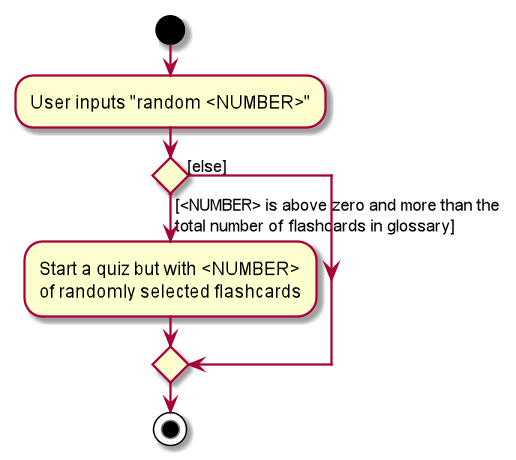
Saving Score History
This feature saves scores from previous rounds of quizzing. It is facilitated by classes in the Command, Model and Storage components.
Scores are encapsulated in the Model by Score objects, which store scoring information that can be retrieved from the following methods:
-
Score#getScore()- Returns the number of flashcards answered correctly in the quizzing round -
Score#getNumQuestions()- Returns the number of flashcards tested in the quizzing round -
Score#getFlashcards()- Returns a list of flashcards tested in the quizzing round
Each time the quiz mode is entered and ended, a Score object is created and added to a ScoreList, where the following methods are implemented:
ScoreList#addScore()ScoreList#getScoreList()
The following activity diagram summarises how scores are incremented:
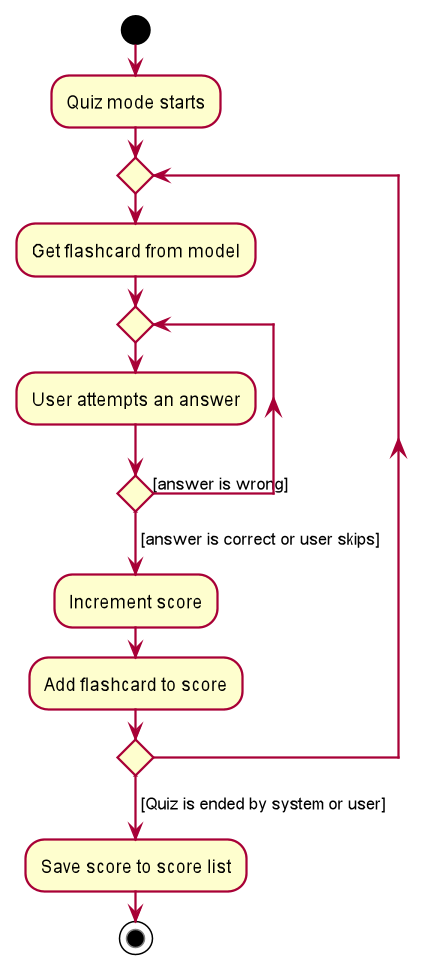
Design Considerations:
Storing Flashcards in each Score:
-
Current Implementation: Each
Scoreobject contains a list of eachFlashcardtested in a round. This is a potentially storage-intensive feature that could result in the same flashcard being saved in multiple scores. This would cause duplication of data in thescores.jsondata storage file. -
Alternative: Currently, the only score information displayed to the user on use of the
scorescommand are:- Number of flashcards answered correctly
- Number of flashcards tested
- List of German phrases tested
Therefore, each
Scoreobject could just store a list of German phrases tested (as Strings) instead of a list ofFlashcards. This reduces storage use as eachFlashcardobject contains additional data fields that are not used in the score history feature, like tags. -
Justification for Current Implementation: Storing all
Flashcards allows possible future extensions of the score history feature, such as:- A feature to test all flashcards associated with a particular score, allowing users to improve their performance
- A feature to display whether each flashcard was answered correctly in a particular round of quizzing. Storing
Flashcards allows this information to easily be added to eachFlashcardas a data field.
Sorting
The Sort feature is implemented as a way for users to further customise their view of the glossary and make it easier for them to find phrases they want.
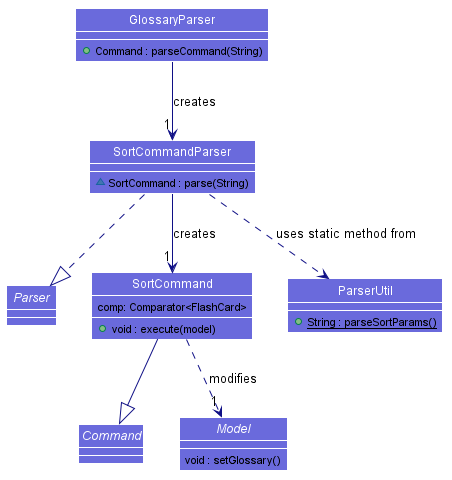
Sorting is implemented as a SortCommand class which extends from the abstract Command class and makes use of a SortCommandParser and GlossaryParser to parse the parameters input by the user.
This is in line with the original AddressBook3’s Command pattern.
SortCommand relies on several pre-defined Comparator objects to execute the sorting, one of which is selected for use when
the user’s input is successfully parsed by SortCommandParser. For example, when the user inputs sort english, a SortCommand object is created
with a Comparator to compare the EnglishPhrases of each FlashCard object in the Glossary.
This class diagram outlines the structure of SortCommand and SortCommand and how they interact with
other aspects of the program.
The following sequence diagram briefly outlines the execution process with respect to the Logic component when a user enters the command “sort english”:
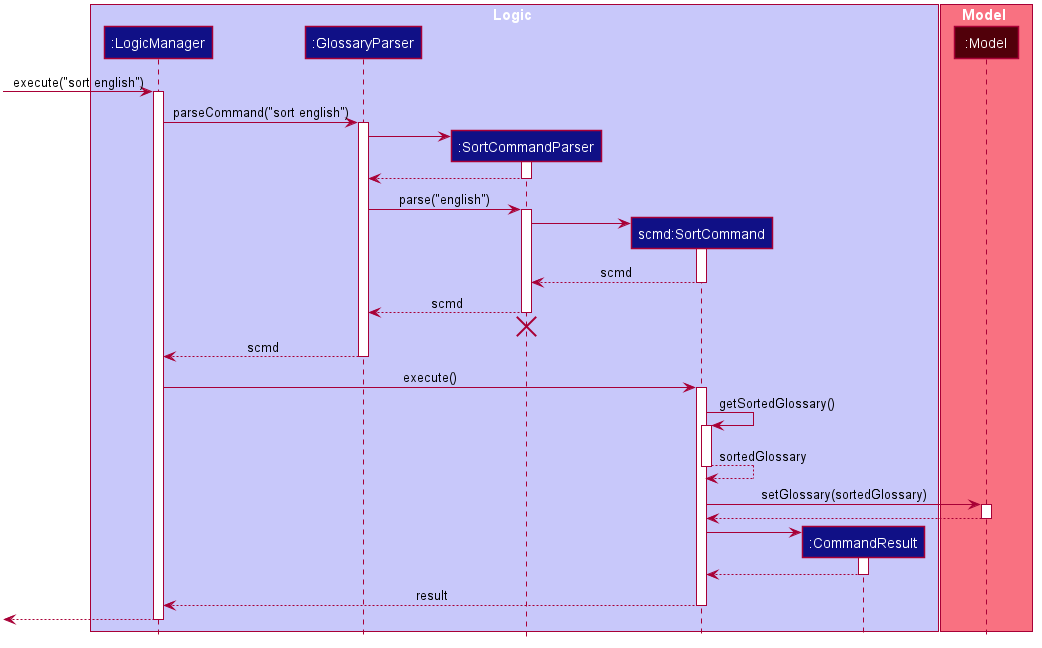
- The user command is first passed into
LogicManager, which calls uponGlossaryParserto parse the command. -
GlossaryParseridentifies the input as a command to sort the glossary, creates aSortCommandParserand calls itsparse(String)method. - The new
SortCommandParserparses the parameter and creates a newSortCommand. -
LogicManagercalls the newSortCommand’sexecute(model)method. -
execute()callsSortCommand’s owngetSortedGlossary()method to obtain a sortedGlossary. - The sorted
Glossaryreplaces the currentGlossaryinModel. - The result of the command execution is encapsulated as a CommandResult object which is passed back to the
Ui.
Note: The lifeline for SortCommandParser should end at the destroy marker (X) but due to a limitation of PlantUML, the lifeline reaches the end of diagram.
Alternatives:
-
Sorting replaces the entire Glossary with a new sorted Glossary (current implementation)
- Pros: Fairly adaptable from existing commands
- Cons: Large glossary size may lead to computational delays and overhead
-
Sorting sorts the current Glossary in place instead of creating a new Glossary
- Pros: Less computational overhead
- Cons: Original AB3 implementation uses immutable Glossary equivalent, requires very significant refactoring of code to achieve. Using a mutable Glossary also makes the code more vulnerable.
Documentation, logging, testing, configuration, dev-ops
Appendix: Requirements
Product scope
Target user profile:
ForgetfulNUS is targeted at students taking level 1000-2000 German language modules (LAG1201 and LAG2201) at the NUS Center of Language Studies who can type fast and prefer typing to mouse interactions.
Value proposition:
A flashcard CLI app designed to cater to the specific needs of the target user to help them learn their German vocabularies.
User Stories
Priorities: High (must have) - * * *, Medium (nice to have) - * *, Low (unlikely to have) - *
| Priority | As a… | I want to… | So that I… |
|---|---|---|---|
| *** | user | add a flashcard with German phrase and meaning | can refer it or use it to test myself later. |
| *** | user | list out all the flashcards with index | can look through the phrases and their meanings to study. |
| *** | user | delete a flash card by index | can remove flashcards that I deem irrelevant. |
| *** | user | test myself with the flashcards | can be quizzed on the phrases and their meanings. |
| ** | user | my flashcards to be saved (storage) | can use them when I next launch the app. |
| ** | user | to sort my flashcards in certain ways | can navigate the glossary more easily. |
| ** | user | test myself with a randomised quiz | can do a quick quiz to jog my memory. |
| ** | user | edit an existing flashcard’s fields | can make any changes to existing flashcards if I want to. |
| ** | user | search for a specific flashcard | can find a specific flashcard more easily. |
| ** | user | save the scores of my previous quizzes | can keep track of my progress easily. |
| ** | user | reset the glossary | can start from scratch with my own personalised data. |
| * | user | be reminded to quiz myself daily | can be reminded to consistently put in effort to revise. |
| * | user | hard reset my score history | can start over from scratch. |
Use Cases
(For all use cases below, the System is ForgetfulNUS and the Actor is the user, unless specified otherwise)
Use Case: UC1 - Add a flashcard
MSS:
- User adds a flashcard with German phrase and meaning.
-
ForgetfulNUS adds the flashcard and display the newly-added flashcard.
Use case ends.
Extensions:
-
1a. ForgetfulNUS detects less than 2 fields for the flashcard.
- 1a1. ForgetfulNUS requests the User to input a German phrase and an English translation for the flashcard.
- 1a2. User enters a new flashcard or terminates the process.
Steps 1a1-1a2 are repeated until the user input is correct or the user terminates the process.
Use case ends.
Use case: UC2 - List all Flashcards
MSS:
- User requests ForgetfulNUS to list all the flashcards.
-
ForgetfulNUS shows the list of flashcards.
Use case ends.
Extensions:
-
1a. ForgetfulNUS detects incorrect command.
-
1a1. ForgetfulNUS shows error and asks for a command in the correct format.
-
1a2. User enters a command.
Use case ends.
-
Use case: UC3 - Delete a Flashcard
MSS:
- User deletes a flashcard by the index.
- ForgetfulNUS deletes the flashcard and displays the information of the deleted flashcard.
Use case ends.
Extensions:
-
1a. User inputs an invalid index (e.g -1)
-
3a1. ForgetfulNUS shows error and asks for a command in the correct format.
-
3a2. User enters a command with the correct format.
Use case ends.
-
Use case: UC4 - Self-testing with Flashcards
MSS:
- User requests to start self-testing.
- ForgetfulNUS displays a German word.
- User inputs the corresponding English translation.
-
ForgetfulNUS displays the results of User’s answer.
Steps 2-4 are repeated until there are no more words to be tested.
Use case ends.
Extensions:
-
2a. User chooses to skip the German word.
-2a1. ForgetfulNUS displays the next German word.
-
3a. User inputs the wrong English translation.
- 3a1. ForgetfulNUS prompts the user to try again.
-
4a. At any time, User chooses to stop self-testing.
- 4a1. ForgetfulNUS stops self-testing.
Use case ends.
Use case: UC5 - Sorting the Glossary
MSS:
- User requests to sort the glossary according to a parameter.
-
ForgetfulNUS sorts the glossary according to the parameter.
Use case ends.
Extensions:
-
1a. The glossary is currently empty.
-
1a1. ForgetfulNUS informs the user that the glossary is empty.
-
1a2. User enters another command.
Use case ends.
-
Use case: UC6 - Self-testing with specified number of randomised Flashcards
MSS:
- User requests to start random self-testing with specified number of flashcards.
- ForgetfulNUS displays a random German word.
- User inputs the corresponding English translation.
-
ForgetfulNUS displays the results of User’s answer.
Steps 2-4 are repeated until the number of flashcards tested has hit the number specified by the user.
Use case ends.
Extensions:
-
2a. User chooses to skip the German word.
-2a1. ForgetfulNUS displays the next random German word.
-
3a. User inputs the wrong English translation.
- 3a1. ForgetfulNUS prompts the user to try again.
-
4a. At any time, User chooses to stop self-testing.
- 4a1. ForgetfulNUS stops self-testing.
Use case ends.
Non-Functional Requirements
- Should work on any mainstream OS as long as it has Java 11 or above installed.
- A user with above average typing speed for regular English text should be able to accomplish most of the tasks faster using commands than using the mouse.
- German diacritics (eg. ä) should be fully supported in being saved and displayed by the UI.
- Verification of user input in testing mode should not take more than 2 seconds.
- Navigating the glossary should not be tedious for the user.
Glossary
- CLI: Command Line Interface
- Mainstream OS: Windows, Linux, Unix, OS-X
- Flashcard: An item containing (a) a German phrase (b) the corresponding English definition (c) an associated Difficulty Tag (d) (optional) an associated Gender Tag (e) (optional) one or more Tags
- German phrase: German text of any length
- Index: Position of flashcard in the list of flashcards displayed to the user
Appendix: Instructions for Manual Testing
Given below are instructions to test the app manually.
Launching and Shutting Down
-
Initial launch
-
Download the jar file and copy into an empty folder
-
Double-click the jar file.
Expected: Shows the GUI with a set of sample flashcards. The window size may not be optimal.
-
-
Saving window preferences
-
Resize the window to an optimal size. Move the window to a different location. Close the window.
-
Re-launch the app by double-clicking the jar file.
Expected: The most recent window size and location is retained.
-
Deleting a Flashcard
-
Deleting a flashcard while all flashcards are being shown
-
Prerequisites: List all flashcards using the
listcommand. Multiple flashcards in the glossary. -
Test case:
delete 1
Expected: First flashcard is deleted from the glossary. Details of the deleted flashcard shown in the status message. -
Test case:
delete 0
Expected: No flashcard is deleted. Error details shown in the status message. Status bar remains the same. -
Other incorrect delete commands to try:
delete,delete x,...(where x is larger than the list size)
Expected: Similar to previous.
-
-
Deleting a flashcard after using
find-
Prerequisites: Multiple flashcards in the glossary.
findcommand is used to filter the list. -
Test case:
delete 1
Expected: First flashcard in the filtered glossary is deleted. Filtered glossary is still shown. Details of the deleted flashcard shown in the status message. -
Test case:
delete 0
Expected: No flashcard is deleted. Error details shown in the status message. Status bar remains the same. -
Other incorrect delete commands to try:
delete,delete x,...(where x is larger than the list size)
Expected: Similar to previous.
-
Sorting Flashcards
-
Sorting the glossary while all flashcards are being shown
-
Prerequisites: List all flashcards using the
listcommand. Multiple flashcards in the glossary. -
Test case:
sort german
Expected: Glossary is sorted according to alphabetical order of the German phrases. -
Other sorting parameters to try:
english,latest,easytohard,reversegerman,...
Expected: Glossary is successfully sorted according to the parameter input.
-
-
Sorting an empty glossary
-
Prerequisites: Glossary is empty (easily done through
clear). -
Test case:
clearto empty the glossary, thensort x(where x can be any sorting parameter) Expected: Error message shown in message box due to empty glossary.
-
-
Sorting the glossary after using
find-
Prerequisites: Multiple flashcards in the glossary.
findcommand is used to filter the list. -
Test case:
sort german
Expected: Filtered list is sorted according to alphabetical order of the German phrases. Original glossary is also sorted. Filtered glossary still shown. -
Other sorting parameters to try:
english,latest,easytohard,reversegerman,...
Expected: Glossary is successfully sorted according to the parameter input. Original glossary is also sorted. Filtered glossary still shown.
-
Viewing Past Scores
- Viewing a non-empty score list
- Prerequisites:
- List all flashcards using the
listcommand. - Have multiple flashcards in the glossary. Ensure your glossary does not already contain a flashcard with German phrase ‘vergesslichkeit’ and English phrase ‘forgetfulness’, as it will be added in this test.
- For simplicity, let the score list be empty (easily achieved through
reset scores).
- List all flashcards using the
-
Test case:
quiz->end quiz->scores
Expected: The score and German phrases tested in this attempt are shown. -
[To be executed immediately after (b)] Test case:
add g/Vergesslichkeit e/forgetfulness->quiz->end quiz->scores
Expected: The score and German phrases tested in this attempt are shown at the top of the list, above the previous attempt. - [To be executed immediately after (c)]
Test case:sort latest->delete 1->quiz->end quiz->scores
Expected: The list of flashcards tested is the same as in (b), so this score is considered a duplicate. The score list displayed will remain the same as in ©.
- Prerequisites:
- Viewing an empty score list
- Prerequisites: Score list is empty (easily done through
reset scores) - Test case:
scores
Expected: A message is shown stating that no past scores have been saved.
- Prerequisites: Score list is empty (easily done through
Saving Data
-
Dealing with missing/corrupted data files
- To simulate a missing glossary file, delete the
glossary.jsonJSON file in the data folder, then launch the program.
Expected: The program successfully launches containing the default sample data. - To simulate a missing score file, delete the
scores.jsonJSON file in the data folder, then launch the program. Expected: The program successfully launches containing an empty score list. - To simulate a corrupted glossary or score file, edit the
glossary.jsonorscores.jsonJSON files to include incorrect JSON syntax. (e.g. Add a line “this is invalid” to the bottom of the file).
Expected: The program successfully launches containing the default sample data, and the old invalidglossary.jsonorscores.jsonis overwritten.
- To simulate a missing glossary file, delete the